The Fundamentals of Debt Coverage Ratio (DCR)


What is a DCR?
The DCR or ‘Debt Coverage Rate’, refers to a Debt-to-income ratio which is a popular benchmark and expresses how many times the income of a property covers the commercial debt on an annual basis. The DCR is used by commercial lenders, and investors to compare the risk factor on the investment. If the ratio is higher, it means the property has a greater ability to cover its financial obligations. If the ratio is lower, it has a lesser ability to cover its financial obligations. The DCR can be also used to quickly determine how much ‘excess cash flow’ the asset might produce.
How do I Determine the DCR?
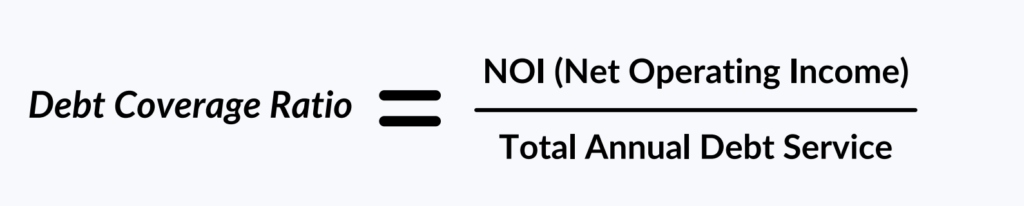
The debt coverage ratio is determined by the Net Operating Income (NOI) divided by the Total Debt Service.
Why Does Debt Service Coverage Matter?
Most importantly, it is a metric on your ability to pay back the loan. This most basic metric will give you a number that can tell if you even have a viable deal. This is a benchmark used by all lenders and most will have a benchmark per loan type that they will require an asset to produce a certain ratio in order to qualify for the loan.
Rules Of Thumb For DCR
Like most investment figures, it is important for you to have a ‘Criteria’ or ‘Rules of thumb’ for your business. If you understand commercial loans, a lot of them share certain benchmarks or criteria that must be met by the property in order to qualify for the loan. The average debt coverage ratio criteria is about 1.25. This is a benchmark used by many lenders which means that the income produced by this property must cover the debt 1.25 times. Remember, this is a minimum benchmark for a lot of lenders which means you should be beyond this in order to achieve a well performing investment. For example, a target of 1.35 or greater in Year 1 is good.
Related posts
Understanding the Distinction Between Asset Management and Property Management in Multifamily Real Estate
Read more
Changes In the Bonus Depreciation Rules and How It Impacts Real Estate Investments
Read more